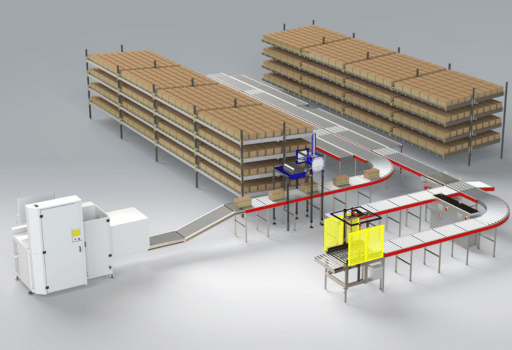
What is a Fully Automated Warehouse System?
A fully automated warehouse system integrates cutting-edge technologies such as robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to handle warehouse operations with minimal human intervention. These systems manage inventory, picking, packing, and shipping processes seamlessly, improving efficiency and accuracy.
Key Components of a Fully Automated Warehouse System
1. Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
AS/RS uses robotics and conveyor systems to store and retrieve items quickly and accurately. These systems maximize space utilization and reduce the time required to access inventory.
2. Robotics and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) navigate warehouses using sensors and AI to transport goods efficiently. These robots eliminate the need for manual labor in transporting heavy loads, enhancing safety and productivity.
3. Warehouse Management Software (WMS)
Advanced WMS solutions integrate with automation systems to manage inventory, track orders, and optimize workflows. AI-driven analytics help predict demand and streamline logistics operations.
4. Internet of Things (IoT) and Real-Time Tracking
IoT devices provide real-time data on inventory levels, environmental conditions, and equipment performance. Smart sensors and RFID tags enhance inventory visibility and minimize losses due to misplacement or theft.
5. Automated Sorting and Packing Systems
AI-powered sorting and packing machines streamline order fulfillment by categorizing, labeling, and packing items efficiently. This reduces errors and speeds up delivery times.
Benefits of Fully Automated Warehouse Systems
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Automation accelerates warehouse processes, reduces downtime, and optimizes workflows, allowing businesses to handle higher order volumes with ease.
2. Cost Reduction
Although automation requires initial investment, it significantly lowers labor costs, minimizes errors, and reduces waste over time.
3. Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Errors
AI-driven systems ensure precise inventory tracking and order fulfillment, reducing mistakes and customer complaints.
4. Improved Safety and Working Conditions
Automated systems eliminate the need for manual heavy lifting, reducing workplace injuries and enhancing safety standards.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Fully automated warehouses can adapt to changing business needs, allowing companies to scale their operations efficiently.
Challenges in Implementing Fully Automated Warehouse Systems
1. High Initial Investment
Automation technology can be costly to implement, requiring significant capital expenditure for robots, software, and infrastructure.
2. Complex Integration
Integrating automation with existing warehouse management systems and supply chain networks can be challenging and time-consuming.
3. Maintenance and Technical Expertise
Regular maintenance and skilled personnel are necessary to keep automated systems running smoothly, which can add to operational costs.
Future Trends in Warehouse Automation
1. AI and Machine Learning Integration
AI-powered systems will continue to refine warehouse processes, enabling predictive analytics and smarter decision-making.
2. Drone and Aerial Robotics for Inventory Management
Drones will play a significant role in conducting inventory checks and monitoring warehouse conditions in real-time.
3. 5G and Edge Computing for Faster Data Processing
The implementation of 5G technology and edge computing will enhance real-time communication between warehouse systems and IoT devices.
Conclusion
The rise of fully automated warehouse systems marks a significant shift in the logistics industry. Companies that invest in automation stand to benefit from increased efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced accuracy. While challenges exist, advancements in AI, robotics, and IoT will continue to drive innovation, making automation a vital component of the future warehouse landscape.